Utility
Polypeptide vaccines are an effective means of combating novel coronavirus variants and are safer than inactivated vaccines. BCEDB collected novel coronavirus B cell linear epitopes and associated Spike protein variation data and lineages information to assist in the development of polypeptide vaccines. Here are two examples of BCEDB database's use.
Case study 1: Spike protein-based epitopes predicted against SARS-CoV-2 through literature mining
Since the end of 2019, SARS-CoV-2 began to spread around the world, causing huge panic. Until now, there are already an enormous number of people infected with SARS-CoV-2 with a continuous increase and intimidating death rate. In order to overcome this common human problem, researchers worldwide are making tremendous efforts to develop the SARS-CoV-2 vaccine or antidote. In previous work, various screening and verification methods were applied to obtain epitopes in each work, however, those predicted epitopes were not complete consistent and lack of evidences from in-vitro and in-vivo experiments. Therefore, it is necessary and useful to identify the most robust regions predicted to harbor epitopes. The epitopes from those robust regions would be more likely to be vaccine candidates.
The BCEDB database can be used to identify B cell linear epitope candidates.It is discovered that B-cell linear epitopes predicted in multiple studies converged to three hotspot regions in the RBD of the Spike protein with the highest peak consisting of B-cell linear epitopes from a single study . The three hotspot regions harbored three B-cell linear epitopes including 'RQIAPGQTGKIADYNYKLPD', 'SYGFQPTNGVGYQ. and 'YAWNRKRISNCVA'.We estimated the antigenicity score of the three B-cell epitopes with VaxiJen v.2.0, and found that 'RQIAPGQTGKIADYNYKLPD' had the highest antigenicity of 1.41, followed by 'SYGFQPTNGVGYQ' of 0.76 and 'YAWNRKRISNCVA' of 0.39.The three B-cell epitopes were then illustrated on the 3D structure of the Spike protein, showing the most exposed region of the Spike protein.Allergen FP 1.0 was used to access the allergenicity of all three epitopes. Toxicity, hydrophobicity, hydropathicity, hydrophilicity and charge of B-cell epitopes were examined through ToxinPred, which based on machine learning technique and quantitative matrix.The result demonstrates that all the epitopes were predicted to be non-toxin and only one allergenic.These three were predicted as non-toxic epitope candidates with high potential for diagnostics and vaccine development.
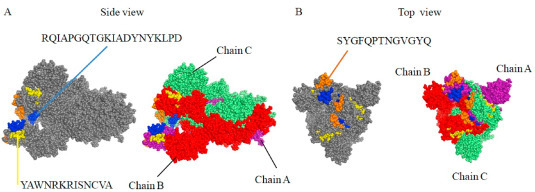
Location of three predicted B-cell epitopes on the 3D structure of the SARS-CoV-2 S protein (PDB ID 6VSB). A. Location of ‘RQIAPGQTGKIADYNYKLPD’ and ‘YAWNRKRISNCVA’. B. Location of ‘SYGFQPTNGVGYQ’. Chain A, B, and C are shown in purple, red and lime color, respectively. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)

The coverage of potential B-cell linear epitopes on the Spike protein. ‘RQIAPGQTGKIADYNYKLPD’, ‘SYGFQPTNGVGYQ’ and ‘YAWNRKRISNCVA’ are the B-cell linear epitopes in hotspot regions in the RBD of the Spike protein.
Case study 2: Epitope-based peptide vaccines predicted against novel coronavirus disease caused by SARS-CoV-2
The emergence of SARS-CoV-2 is a serious health threat for the whole society, thus there is an urgent need for drugs and preventative measures.It is essential to identify immune epitopes as quickly as possible.In this study, we characterized the physio-chemical characteristics of the SARS-CoV-2 viral genome for epitope candidates and adopted an immune-informatics based pipeline with highly stringent criteria to identify S, M and N protein targeted B- and T-cell epitopes that may potentially promote an immune response in the host.The antigenicity, flexibility, solvent accessibility, disulfide bonds of predicted epitopes were evaluated, yielding a small repertoire of potential B-cell epitope and vaccine candidates.Allergenicity and toxicity analysis suggested the ten linear B-cell epitopes in RBD region are of non-allergen and non-toxin.Stability analysis revealed that they cannot be digested by multiple enzymes.Conservation anlaysis of seven known coronaviruses revealed that RBD region is not conserved.Mutations generated from 51,150 sequences of SARS-CoV-2 in the NGDC database were observed in five of ten linear B-cell epitopes in RBD region.The B-cell epitopes without mutations would be considered to be vaccine candidates with full potentials of being antigenicity.
Citation:[1] Li W , Li L , Sun T , et al. Spike protein-based epitopes predicted against SARS-CoV-2 through literature mining[J]. Medicine in Novel Technology and Devices, 2020, 8.
[2] Li L , Sun T , He Y , et al. Epitope-based peptide vaccines predicted against novel coronavirus disease caused by SARS-CoV-2[J]. Virus Research, 2020, 288:198082.