Welcome to GNIFdb!
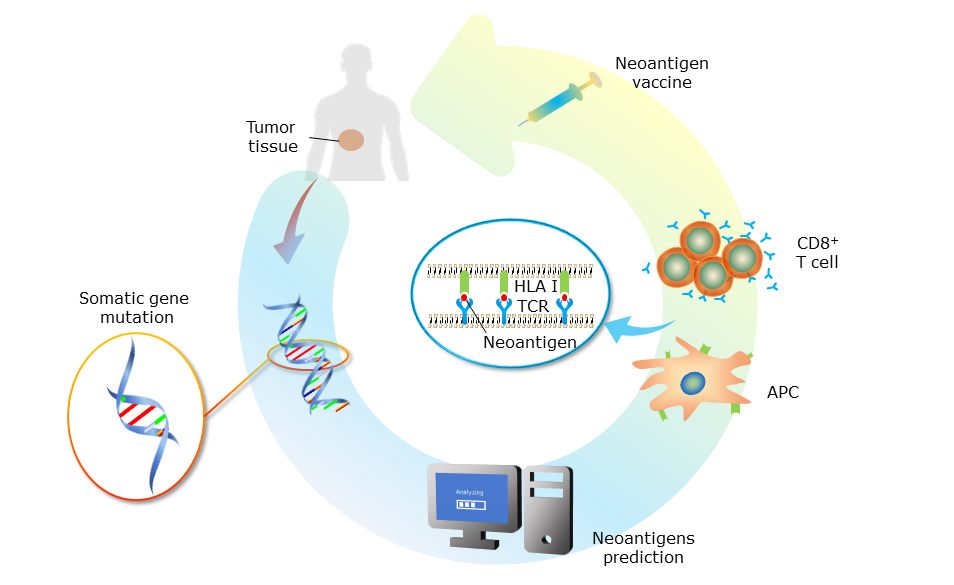
GNIFdb is a comprehensive neoantigen intrinsic feature database in glioma. Neoantigens, classically regarded as being derived from mutation-containing proteins that generate novel immunogenic epitopes, are the attractive targets in personalized immunetherapies, promoting tumor-specific T-cell responses and affecting antitumor immune responses. The intrinsic features of neoantigens are characterized by different Amino Acid (AA) descriptors and physical-chemical properties. The diverse intrinsic features of neoantigens are highly associated with clinical information, which could be used to identify patients who most likely benefit from neoantigen-based personalized immunetherapy.
GNIFdb provides 12,865,632 intrinsic features of 4394 neoantigens (2928 intrinsic features for each neoantigen) covering 20 glioma subtypes from western (TCGA) and asian population. Additional four cancers with neoantigens available are also deposited in GNIFdb, including lung cancer (2619 neoantigens), melanoma (21108 neoantigens), bladder cancer (1250 neoantigens), head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (313 neoantigens). In addition, GNIFdb contains neoantigen peptide sequence, neoantigen associated mutation information, gene expression, human leukocyte antigen (HLA), and HLA binding affinity. All these information can be accessed through visualization platform in GNIFdb.
GNIFdb hosts search engine and tools for neoDL (neoantigen intrinsic feature-based deep learning model), gene enrichment analysis (Normalized Enrichment Analysis, NES) and intrinsic feature calculation.
We calculated 66 amino acid descriptors and physical-chemical properties (aliphatic, auto-correlation, auto-covariance, Boman index, theoretical net charge, cross-covariance, hydrophobic moment, hydrophobicity, instability, molecular weight,Tiny, Small, Aliphatic, Aromatic, Non-polar, Polar, Charged, Basic, Acidic) in different positons of each neoantigen peptide. You can get all the features(2928 features for one neoantigen) in Browse page and calculate the features of your own data in Tools pages. You can click here to see the introduction of all the features.
Cohort 1 includes predicted neoantigens from 733 glioma patients in TCGA-LGG and TCGA-GBM.
Glioma Subtypes Classification by Molecular Profile
Glioma Subtypes Classification by Histological Criteria
Glioma Subtype Data Introduction
Cohort 2 includes predicted neoantigens from 46 GBM patients in Asian populations.
Gene Mutation
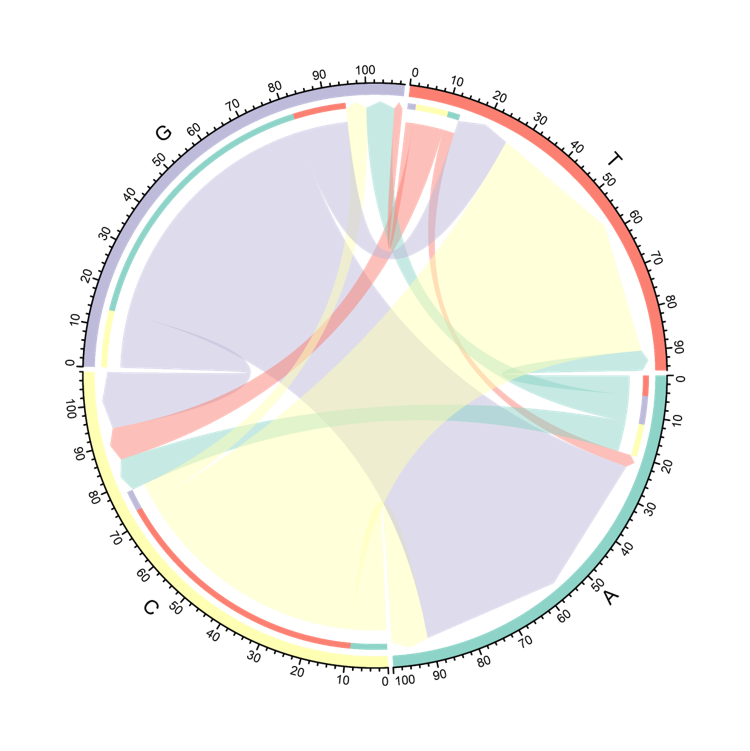
The Circos displays the changes of nucleotide at mutated site included in the neoantigens. The arrow is the nucleotide before and after a mutation occurs. The thickness of the arrow is the number of neoantigens harboring this mutation.
Amino Acid Mutation
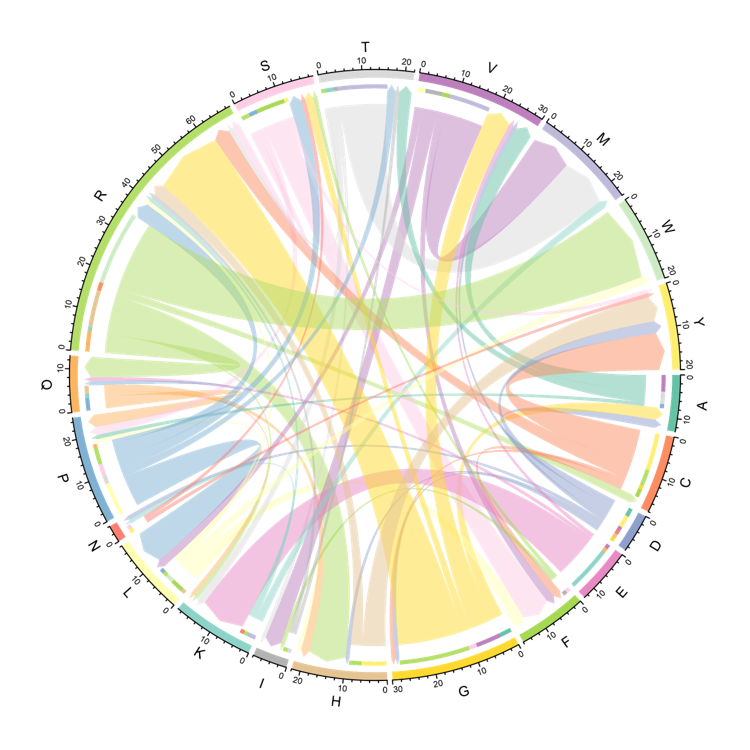
The Circos displays the changes of Amino Acid at mutated site included in the neoantigens. The arrow is the Amino Acid before and after a mutation occurs. The thickness of the arrow is the number of neoantigens harboring this mutation.
Cohort 3 includes predicted neoantigens from 13 GBM patients.
Gene Mutation
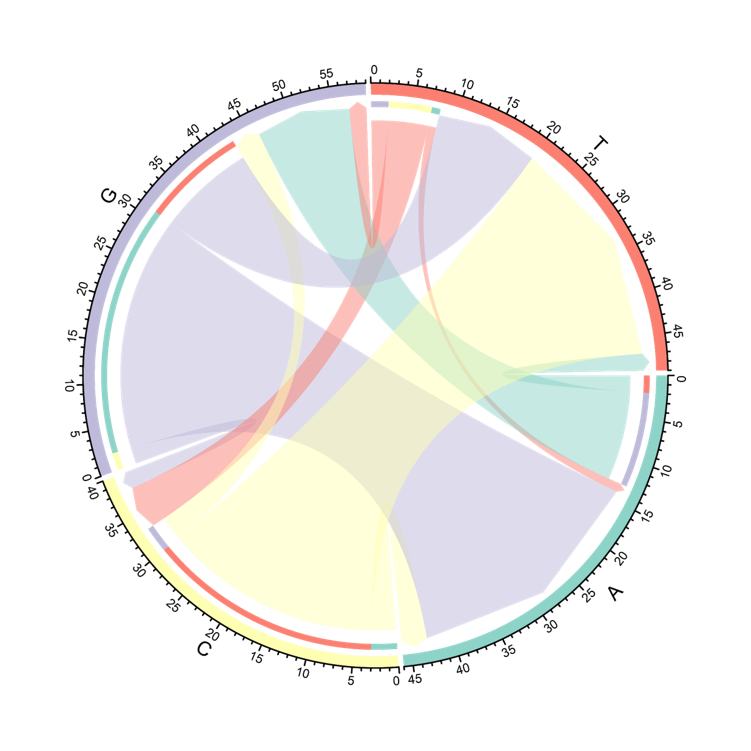
The Circos displays the changes of nucleotide at mutated site included in the neoantigens. The arrow is the nucleotide before and after a mutation occurs. The thickness of the arrow is the number of neoantigens harboring this mutation.
Amino Acid Mutation
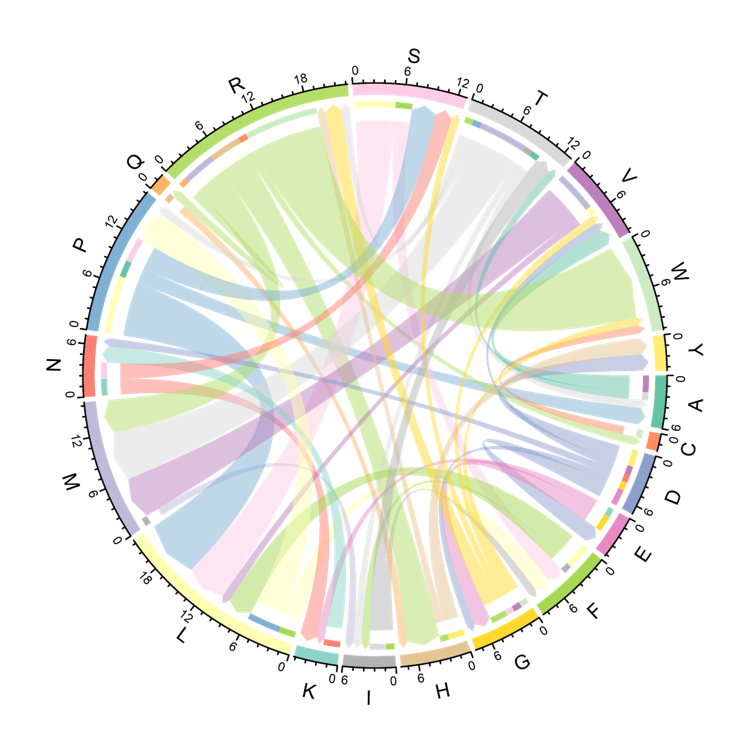
The Circos displays the changes of Amino Acid at mutated site included in the neoantigens. The arrow is the Amino Acid before and after a mutation occurs. The thickness of the arrow is the number of neoantigens harboring this mutation.
Cohort 4 includes:
Lung Cancer: 57 patients HNSCC: 12 patients Melanoma: 151 patients Bladder: 27 patients
Melanoma